Tank heads are used as endcaps on cylindrical tanks, drive cylinders, distillation towers, reactors, gas storage tanks, and more. Tank heads often adhere to ASME standards or other comparable codes. Tank heads are crucial pressure vessel structural components that can hold dangerous or extremely volatile compounds. The integrity of the tank and tank head is preserved through correct design and construction. Read More…
At Ace Metal Spinning, we believe in creating products that precisely meet our customers' specifications. If you need a unique part, we can make it for you. We also provide in-house tooling to keep your costs low. It is our goal to benefit our customers however we can through our service, products, and prices. Learn more on our website today!

Our CNC spinning equipment are fully automated machines and capable of sheet metal spinning, trimming and beading all in one process. Copper spinning and aluminum spinning symmetrically round items is what we do most. Stainless Steel spinning is very popular for the pharmaceutical and food service parts we make. If you need to produce a symmetrical metal part without seams and with minimal...

At Stuecklen Manufacturing Company, we take pride in our long-standing expertise in the art and science of metal spinning. Since our founding, we have dedicated ourselves to combining traditional craftsmanship with modern technology to produce precision-formed components that meet the highest standards of quality and performance.

At Sundry Metal Spinning, we specialize in providing comprehensive solutions for metal spinning, catering to the diverse needs of industries worldwide. With our commitment to excellence and extensive experience, we have established ourselves as a trusted partner for customers seeking high-quality and precise metal spinning services. Our metal spinning capabilities encompass a wide range of...

In business since 1944, Muncie Metal Spinning has been a metal spinning company offering tanks, air cleaners, sump breather tanks, fill cans and much more. In addition, we do custom ornamental metal spinning from aluminum, copper or brass, welding, shearing, and prototype development. Call us today for more information or visit our website and request a quote!

More Tank Head Companies
Tank heads are essential components in the fabrication of pressure vessels, storage tanks, and various types of industrial containers. Tank heads are frequently coated, heat-treated, or constructed with stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, or specialty alloys to meet demanding application requirements. Selecting the correct material and finish is critical for corrosion resistance, durability, and compliance with industry standards such as ASME, API, and ISO.

Types of Tank Heads
Understanding the various tank head designs is essential for engineers, fabricators, and procurement professionals seeking optimal performance, safety, and cost efficiency. The main types of tank heads are:
Hemispherical Heads
The hemispherical head is regarded as the strongest shape for a tank or pressure vessel end. This spherical form distributes stress evenly throughout the material, significantly reducing the risk of failure under pressure. The radius of the cylindrical vessel matches the radius of the head, creating a seamless, high-integrity boundary for containing pressurized contents. Hemispherical heads are ideal for applications requiring maximum strength-to-weight ratios, such as high-pressure storage tanks, gas cylinders, and chemical reactors.
These heads are commonly referred to as "dish ends" in the industry and are prized for their ability to withstand internal pressure efficiently. Their geometry allows for a larger maximum radial section, which translates into superior pressure distribution and durability, making hemispherical heads a standard choice for critical applications. The robust construction and pressure-handling capacity also make them suitable for the oil and gas, pharmaceutical, and food processing sectors.

Torispherical Tank Heads
Torispherical heads—sometimes called "flanged and dished heads"—feature a combination of a large crown radius with a small knuckle radius and a straight flange at the base. This design is the most widely used for pressure vessel heads due to its balance between strength and manufacturability. The torispherical shape provides a wider radial section than ellipsoidal heads, creating an even distribution of pressure and enabling these heads to handle significant internal forces.
While torispherical heads are more expensive to fabricate than certain alternatives, they offer time savings in production and are easier to install, particularly for vessels with moderate pressure requirements. Industries such as petrochemical processing, water treatment, and industrial gas storage often specify torispherical heads for their combination of reliability, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with safety codes.

Flat Heads
Flat heads and flat-sloping heads are straightforward and economical to manufacture, commonly used for vessels with smaller diameters operating under low internal pressure. They are constructed flush with the tank wall, making them suitable for atmospheric storage tanks, water tanks, and vessels where pressure containment is not a primary concern. However, flat heads offer limited resistance to pressure compared to dished or hemispherical designs.
Due to their geometry, flat heads receive a higher concentration of stress and are more susceptible to deformation or failure under load. They are generally not recommended for high-pressure applications but are popular for cost-sensitive projects and non-critical service. When deciding between flat and dished tank heads, evaluating the vessel's pressure requirements, material costs, and long-term maintenance needs is essential.

Ellipsoidal Heads
Ellipsoidal heads (also called elliptical or 2:1 elliptical heads) are a cost-effective compromise between hemispherical and torispherical designs. Their height is typically one-quarter of the vessel's diameter, which lowers material usage and overall fabrication costs. Despite their relatively shallow profile, ellipsoidal heads maintain good strength and pressure resistance, making them a popular choice for medium and high-pressure vessels.
These heads feature a square flange and a knuckle, providing ease of installation and integration with cylindrical shells. While the pressure distribution is not as uniform as that of a torispherical head, ellipsoidal heads offer a strong balance between structural integrity and manufacturability. They are favored in industries such as beverage production, dairy processing, and chemical storage where both cost and performance are critical decision factors.

Toriconical Heads
Toriconical heads are designed with a wide base at the shell and a tapering, conical head that improves flow characteristics inside the vessel. At the wide end of the cone, these heads feature a knuckle and a straight flange for ease of welding and assembly. The toriconical shape is particularly valued in process industries where solids or liquids must be directed toward a vessel outlet, such as in hoppers, silos, and certain reactors.
Although toriconical heads cost more to produce due to their complex geometry, their design promotes self-cleaning, reduces product buildup, and enhances process efficiency. Industries requiring hygienic standards, such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology, often specify toriconical heads to meet regulatory and operational needs.

Applications and Benefits of Tank Heads
Tank heads play a crucial role in a vast array of industries and applications. Their proper selection and installation are vital for ensuring process safety, operational longevity, and regulatory compliance. Common applications and advantages include:
- Pressure autoclaves in the medical profession rely on robust tank heads to maintain sterilization conditions and ensure user safety.
- Petroleum tanks and water tanks depend on high-quality tank heads to prevent leakage, contamination, and product loss during storage and transport.
- Tank heads serve as critical containment solutions, preventing spills, contents loss, and environmental hazards in chemical processing, food & beverage, and wastewater treatment industries.
- Compressors and refrigerant storage vessels utilize tank heads to contain liquid and gaseous media under pressure, enabling efficient operation and safeguarding against hazardous releases.
- Properly specified tank heads can reduce expenses by optimizing material usage, minimizing downtime, and extending the service life of pressure vessels and storage tanks.
- Tank heads are engineered to guarantee the security of personnel and equipment, supporting compliance with safety standards and minimizing liability risks.
- In applications such as pharmaceutical manufacturing, food and beverage processing, and specialty chemical production, tank heads ensure product purity and process reliability.
- Specialty tank heads, such as those with custom nozzles, manways, or sanitary finishes, are tailored to meet unique process requirements and enhance operational efficiency.
Key Factors in Selecting the Right Tank Head
Choosing the optimal tank head for your pressure vessel or storage tank project involves careful consideration of several critical factors. These decision points will help you achieve the best balance of safety, performance, regulatory compliance, and cost-effectiveness:
- Application requirements: What is the primary function of the vessel—pressure containment, storage, mixing, or process transfer? The intended use will determine the best head shape and material.
- Pressure rating and design code: Evaluate the maximum operating pressure and applicable codes (e.g., ASME Section VIII, API 650/620, PED). Higher pressures typically require hemispherical or ellipsoidal heads.
- Material compatibility: Consider the chemical properties of stored media and select materials that resist corrosion, stress cracking, or product contamination (e.g., stainless steel, carbon steel, aluminum, nickel alloys).
- Size and thickness: The vessel’s diameter, wall thickness, and overall dimensions will impact the manufacturability and cost of the tank head. Larger diameters may require segmented or fabricated heads.
- Finish and coatings: For sanitary or corrosive environments, specify polished finishes, linings, or coatings such as epoxy, PTFE, or glass-lined steel.
- Thermal performance: In applications involving temperature extremes, ensure the tank head design accommodates thermal expansion, contraction, and insulation requirements.
- Integration features: Customizations such as manways, nozzles, sight glasses, or sensor ports may be required for process monitoring and maintenance.
- Budget and lead time: Factor in the cost of raw materials, fabrication complexity, and delivery schedules to ensure project timelines and budgets are met.
These decision points should be discussed with your engineering team, vessel fabricator, and tank head supplier to ensure optimal results.
Common Industries and Use Cases for Tank Heads
Tank heads are indispensable in a wide range of industries and serve as critical components in both standard and custom vessel designs. Some of the main sectors and use cases include:
- Oil & Gas: Storage and transport vessels, separators, pressure vessels, and flare stacks.
- Chemical Processing: Reactor vessels, mixing tanks, and hazardous material containment.
- Pharmaceuticals: Sterile process vessels, autoclaves, and sanitary storage tanks.
- Food & Beverage: Fermenters, brew kettles, pasteurizers, and sanitary storage containers.
- Power Generation: Boiler drums, condensate tanks, and steam accumulators.
- Water Treatment: Filtration vessels, clarifiers, and potable water storage tanks.
- Aerospace & Defense: Propellant tanks and high-pressure containment systems.
- HVAC & Refrigeration: Chiller tanks, accumulator vessels, and refrigerant receivers.
- Mining & Minerals: Slurry tanks, thickener tanks, and process holding vessels.
Each industry may require specific tank head features such as corrosion resistance, sanitary finishes, or compliance with strict regulatory codes. Custom fabrication and engineering support are often necessary to meet these sector-specific demands.
Manufacturing Methods and Quality Considerations
The manufacturing process for tank heads varies according to their size, shape, material, and end-use application. The primary fabrication methods include:
- Cold forming (spinning, pressing): Suitable for thin-walled, small- to medium-diameter heads. Cold forming preserves material properties and ensures precise tolerances.
- Hot forming (pressing, spinning): Used for thicker materials or heads with complex geometries. Hot forming can relieve internal stresses and enable the creation of large, heavy-duty heads.
- Segmented fabrication: For extra-large diameters, heads may be constructed from welded segments or petals, then finished to meet strength and leak-tightness specifications.
- Machining and finishing: After forming, heads may be machined, ground, or polished to achieve required surface finishes, sanitary standards, or dimensional tolerances.
Quality assurance is essential throughout the manufacturing process. Reputable tank head suppliers will perform rigorous testing and inspections such as hydrostatic testing, ultrasonic testing, material certification, and dimensional verification to ensure compliance with engineering drawings and applicable codes.
How to Specify a Tank Head for Your Application
When requesting a quote or placing an order for a tank head, it’s important to supply detailed specifications to your supplier or fabricator. Consider including the following information:
- Head type (hemispherical, torispherical, ellipsoidal, flat, or toriconical)
- Material grade and finish requirements
- Diameter, thickness, and height/depth
- Design pressure and temperature
- Required certifications or compliance codes (e.g., ASME, PED, API)
- Special features (manways, nozzles, custom openings, internal linings)
- Quantity and delivery timeline
Providing detailed requirements upfront will help your tank head supplier deliver the optimal solution for your project, minimize lead times, and ensure cost-effective manufacturing.
Choosing the Correct Tank Head Supplier
To ensure you have the most positive outcome when purchasing a tank head from a tank head supplier, it is important to compare several companies using our directory of tank head suppliers. Each tank head supplier has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the supplier for more information or request a quote. Review each tank head business website using our patented website previewer to quickly learn what each company specializes in. Then, use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple tank head suppliers with the same form.
When evaluating tank head manufacturers and suppliers, consider the following best practices:
- Assess the supplier’s experience with your industry and specific vessel requirements.
- Review their quality control certifications (ASME, ISO, PED) and manufacturing capabilities (material range, head sizes, finishing options).
- Request documentation of past projects, customer references, and example test reports.
- Discuss lead times, logistics, and after-sales support, including engineering assistance and repair services.
- Ensure transparency in pricing, including material costs, fabrication charges, and delivery fees.
- Choose suppliers who demonstrate a strong commitment to safety, compliance, and customer satisfaction.
By following these guidelines and leveraging our supplier directory, you can confidently navigate the process of sourcing the ideal tank head for your next project—whether it’s a high-pressure reactor, sanitary storage vessel, or custom-fabricated tank for specialized applications.
Frequently Asked Questions About Tank Heads
What are the main differences between tank head types?
Tank heads vary by shape, pressure rating, and manufacturing cost. Hemispherical heads offer maximum strength but are more costly, ellipsoidal heads provide a good balance of strength and economy, torispherical heads are common for pressure vessels, flat heads suit low-pressure applications, and toriconical heads are selected for ease of material flow in process vessels.
How do I determine the correct material for my tank head?
Material selection depends on stored media, operating pressure and temperature, corrosion resistance needs, and regulatory requirements. Common options include carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and high-nickel alloys. Consult with your engineering team and supplier for specific recommendations.
Are there standard sizes and dimensions for tank heads?
Many tank heads are manufactured to industry standards (such as ASME or API), but custom sizes are also available to suit unique vessel configurations. Providing detailed specifications to your supplier ensures accurate fit and performance.
Can tank heads be customized for special applications?
Yes, tank heads can be fabricated with custom features such as manways, access ports, nozzles, reinforcement pads, and specialty linings or coatings. Customization supports unique process needs and regulatory compliance.
What quality tests are performed on tank heads?
Reputable manufacturers perform hydrostatic testing, ultrasonic inspection, dimensional checks, and material verification to ensure tank heads meet engineering drawings and applicable codes. Always request quality documentation from your supplier.
Conclusion: Maximizing Value and Safety with the Right Tank Head
Choosing the right tank head is a critical decision that impacts the safety, efficiency, and operational life of your pressure vessel or storage tank. By understanding the various types of tank heads, their applications, and the key criteria for selection, you can make informed decisions that align with your project’s technical and budgetary requirements. Whether you need a standard head for a water tank or a custom-engineered solution for a high-pressure reactor, working with an experienced, quality-focused supplier is essential to achieving the best results.
For additional guidance, comparisons, and sourcing support, utilize our directory and expertise to find the perfect tank head for your next project.









 Cold Headed Parts
Cold Headed Parts Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals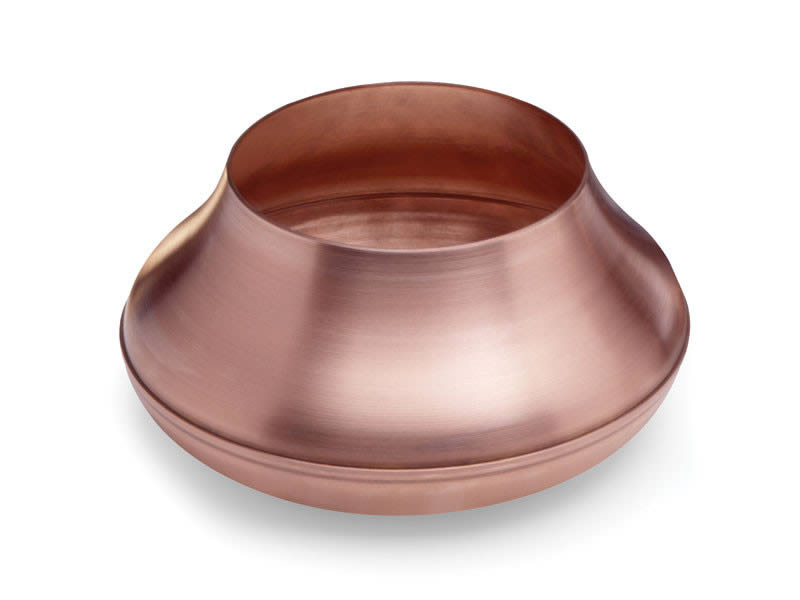 Metal Spinning
Metal Spinning Powdered Metal Parts
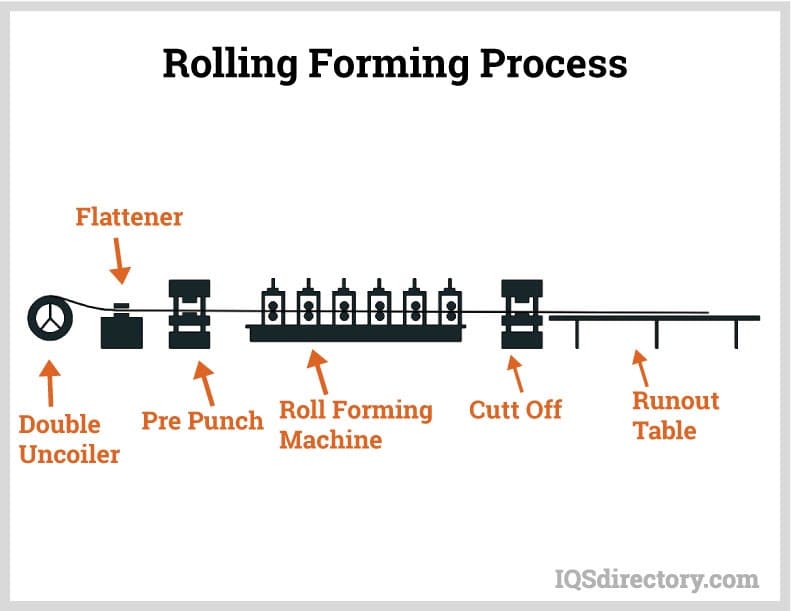
Powdered Metal Parts Roll Forming
Roll Forming Springs
Springs Wire Forms
Wire Forms Wire Mesh
Wire Mesh Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services