Hydroforming is an efficient and specialized molding process that uses highly pressurized fluid to form metals. Hydroforming’s metal fabrication and forming process can shape steel, stainless steel, copper, aluminum, and brass. The ability to preserve high-quality surfaces for finishing and seamless bonding are some advantages of hydroforming. Hydroformed parts have a higher stiffness-to-weight ratio, are more affordable per unit, and are lighter than conventional metal stamped and welded parts. Hydroforming can also produce components in a single step, saving time, resources, and materials. Read More…
At Ace Metal Spinning, we believe in creating products that precisely meet our customers' specifications. If you need a unique part, we can make it for you. We also provide in-house tooling to keep your costs low. It is our goal to benefit our customers however we can through our service, products, and prices. Learn more on our website today!

At Stuecklen Manufacturing Company, we take pride in our long-standing expertise in the art and science of metal spinning. Since our founding, we have dedicated ourselves to combining traditional craftsmanship with modern technology to produce precision-formed components that meet the highest standards of quality and performance.

At Sundry Metal Spinning, we specialize in providing comprehensive solutions for metal spinning, catering to the diverse needs of industries worldwide. With our commitment to excellence and extensive experience, we have established ourselves as a trusted partner for customers seeking high-quality and precise metal spinning services. Our metal spinning capabilities encompass a wide range of...

In business since 1944, Muncie Metal Spinning has been a metal spinning company offering tanks, air cleaners, sump breather tanks, fill cans and much more. In addition, we do custom ornamental metal spinning from aluminum, copper or brass, welding, shearing, and prototype development. Call us today for more information or visit our website and request a quote!

More Hydroforming Companies

Types of Hydroforming
Hydroforming is an advanced metal forming process that utilizes high-pressure hydraulic fluid to shape ductile metals, such as aluminum, stainless steel, copper, and brass, into complex and precise geometries. The hydroforming technique is widely recognized in the metal fabrication, automotive, aerospace, and industrial manufacturing sectors for its ability to produce lightweight, structurally robust, and intricately shaped parts that are often difficult or impossible to create using traditional stamping or welding methods. Understanding the main types of hydroforming is essential for choosing the optimal solution for your specific manufacturing application.
Sheet Hydroforming
Sheet hydroforming is a versatile metal forming process that uses a single, unmatched tool, coupled with a pressurized hydraulic fluid encased in a flexible diaphragm, to shape sheet metal into precise forms. This innovative approach allows manufacturers to combine or even replace a variety of sheet metal forming techniques, including progressive die forming, press brake forming, classic draw forming, and rubber pad forming. As a result, sheet hydroforming streamlines manufacturing by enabling multiple operations in a single cycle, often eliminating the need for costly and time-consuming secondary finishing procedures such as welding, annealing, deburring, or polishing.
Manufacturers frequently turn to sheet hydroforming for applications requiring tight tolerances, intricate shapes, and consistent quality. It is well-suited for industries where high strength-to-weight ratios, aerodynamic performance, and aesthetic surface finishes are crucial, such as in automotive body panel fabrication, aerospace skin panels, and specialized architectural metalwork.

Fluid Cell Sheet Hydroforming
Fluid cell sheet hydroforming is a specialized variant that excels at producing parts with intricate bends, curves, and complex geometries. In this process, a blank sheet of material is placed atop a single, fixed-form block or tool resting on the lower plate of the press. The upper chamber contains a pressurized hydraulic fluid within a flexible diaphragm, which evenly distributes pressure across the entire surface of the part. This uniform application of pressure ensures that the metal conforms precisely to the tool’s contours, resulting in almost net-shaped components that require little or no secondary finishing.
Fluid cell hydroforming is renowned for its ability to form deep-drawn, seamless, and high-strength metal parts used in the aerospace, defense, and high-performance automotive industries. It also offers rapid prototyping capabilities, cost-effective low- to medium-volume production, and flexibility in material selection, making it a preferred solution for manufacturers seeking to reduce tooling costs and accelerate product development cycles.
Deep Draw Sheet Hydroforming
Deep draw hydroforming is an advanced process wherein sheet metal is both stretched and bent simultaneously to achieve significant depth and complex three-dimensional shapes. The process begins with a flat blank, which is placed over a die cavity and held in place by a blank holder. A punch then descends onto the blank, forcing it into the die and forming a cup-like or tubular shape. The key advantage of deep draw hydroforming is its ability to create seamless, high-strength structures with uniform wall thickness, even in ductile metals such as mild steel, copper, aluminum, and stainless steel.
Typical applications of deep draw hydroforming include the production of pressure vessels, automotive fuel tanks, appliance housings, cookware, and electronic enclosures. Manufacturers value this process for its efficiency, accuracy, and ability to reduce material waste while maintaining exceptional structural integrity in finished components.

Tube Hydroforming
Tube hydroforming is a widely adopted metal forming process used to create complex, lightweight, and high-strength tubular components. By applying internal hydraulic pressure and axial force to a metal tube placed inside a die, manufacturers can form parts with intricate contours and varying cross-sectional shapes without thinning or tearing the material. Tube hydroforming is especially beneficial for producing structural automotive components, such as engine cradles, chassis rails, suspension arms, and exhaust system parts, as well as bicycle frames, HVAC ductwork, and specialty piping systems.
This technology enables engineers and designers to reduce part count, minimize welding, and achieve superior mechanical properties. The result is greater design flexibility, improved weight savings, and enhanced crashworthiness in automotive and aerospace applications.
Steps to Tube Hydroforming
The tube hydroforming process involves several key stages:
- Tube Preparation: The raw tube is cut to length and, if required, bent using a tube bender to achieve the desired preform shape. This preparation ensures that the tube fits precisely within the forming dies.
- Die Loading: The pre-bent tube is placed into the hydroforming die, which defines the final geometry of the part.
- Sealing and Fluid Filling: The ends of the tube are sealed, and a hydraulic fluid is introduced into the tube, filling the interior cavity.
- Pressurization and Forming: The hydroforming press applies high internal pressure, causing the tube to expand and conform tightly to the die walls. In some cases, thrust actuators provide additional force to assist in shaping the tube along its length.
- Finishing Operations: Once formed, the hydroformed part may undergo additional operations such as precision laser cutting, hole punching, stenciling, or a parts wash to remove any residual forming lubricant and prepare the component for assembly or surface finishing.

Benefits of Hydroforming
Hydroforming offers a range of significant advantages over traditional metal forming methods such as stamping, forging, and welding. As manufacturing industries seek to optimize performance, reduce costs, and deliver high-quality, lightweight components, hydroforming has emerged as a preferred solution. Here are some of the key benefits that hydroforming delivers to manufacturers, designers, and end-users:
- Complex Geometries with Fewer Welds: Hydroforming enables the creation of intricate, lengthy, and contoured metal shapes with minimal or no welding. This reduces the risk of weak points, enhances structural integrity, and increases efficiency by eliminating the need to join multiple sections.
- Streamlined Production Cycles: The hydroforming process can be completed rapidly, often in 20 seconds or less from tube loading to final product unloading. This speed allows for higher throughput, shorter lead times, and the seamless integration of hydroformed components into larger assemblies.
- Exceptional Dimensional Accuracy: Computer-controlled hydraulic systems regulate forming pressures within ten-thousandths of an inch, ensuring unparalleled precision and repeatability. This high level of accuracy is critical for applications demanding tight tolerances, such as aerospace skin panels and high-performance automotive parts.
- Material and Cost Savings: By consolidating multiple components into a single hydroformed part, manufacturers can dramatically reduce material waste, eliminate redundant processes, and lower overall production costs. Additionally, the process allows for the use of thinner-walled materials without sacrificing strength.
- Lightweight, High-Strength Components: Hydroforming allows for the formation of thinner-walled structures that retain the necessary stiffness and durability. This is especially valuable in automotive and aerospace sectors, where weight reduction translates to improved fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and enhanced vehicle performance.
- Design Flexibility: The process supports the creation of complex, seamless structures with integrated features such as inlet and outlet openings, mounting tabs, and reinforcing ribs. This flexibility enables engineers to innovate and optimize product designs for specific performance requirements.
- Reduced Tooling Requirements: With fewer sections and the elimination of secondary operations like burring and punching, the number of required tools and dies is minimized. This translates to lower setup costs, faster changeovers, and easier adaptation to design modifications.
- Superior Surface Finish: The even distribution of hydraulic pressure during hydroforming yields smooth, blemish-free surfaces that often require little or no post-processing, reducing labor and finishing expenses.
Common Applications and Industry Use Cases
Hydroforming’s unique combination of design flexibility, structural integrity, and material efficiency has made it a go-to solution for a variety of demanding industries. Below are several key application areas where hydroforming delivers significant value:
- Automotive Manufacturing: Hydroforming is widely used to produce lightweight chassis components, engine cradles, exhaust manifolds, suspension arms, and body structural parts. Its ability to reduce part count and integrate complex features leads to cost savings and improved vehicle performance.
- Aerospace & Defense: In aerospace, hydroforming is essential for fabricating seamless skin panels, support structures, and fuel or hydraulic system components, where strength-to-weight ratio and precision are critical. Defense contractors rely on hydroformed parts for lightweight armor, frames, and structural assemblies.
- Bicycle & Sports Equipment: Manufacturers of high-performance bicycles and sporting goods leverage tube hydroforming to create strong, aerodynamic frames and components with minimal weight, enhancing speed and maneuverability.
- Appliance & Consumer Goods: Hydroformed enclosures, handles, and housings are common in appliances, electronics, and industrial equipment, offering aesthetic appeal and robust protection for sensitive internals.
- Medical Devices: The process is ideal for producing surgical instruments, implantable device housings, and specialized tubing, where precision, biocompatibility, and seamless construction are paramount.
- Architectural & Industrial Structures: Hydroforming enables the creation of custom metal panels, decorative trims, and supporting frameworks used in architectural facades, public infrastructure, and industrial machinery.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Hydroforming Services
Selecting the right hydroforming company is a critical decision that impacts part quality, lead times, total cost of ownership, and project success. When evaluating hydroforming suppliers, it’s important to consider several key factors that align with your production goals, technical requirements, and business objectives:
- Experience and Technical Expertise: Look for manufacturers with a proven track record in hydroforming, especially with your target materials (such as aluminum, stainless steel, copper, or exotic alloys) and desired part geometries. Ask about their familiarity with the latest hydroforming equipment, CAD/CAM design capabilities, and quality assurance protocols.
- Production Capacity and Lead Time: Evaluate whether the supplier has the scale and flexibility to accommodate your volume requirements—from rapid prototyping and low-volume runs to full-scale production. Consider their ability to meet tight deadlines and adapt to changes in demand.
- Tooling and Engineering Support: Assess the company’s in-house tooling design and fabrication capabilities. Does the supplier provide comprehensive engineering support, including design optimization, simulation, and prototyping services that can reduce time-to-market and improve final part quality?
- Quality Control and Certifications: Ensure the hydroforming company adheres to strict quality management standards, such as ISO 9001 or industry-specific certifications (TS16949 for automotive, AS9100 for aerospace, etc.). Inquire about their inspection processes, traceability, and documentation practices.
- Material Sourcing and Customization: The ability to source, process, and work with a wide range of metals and alloys is essential. Look for partners that offer customization options, including material selection, part finishing, and secondary operations such as machining, welding, and coating.
- Cost Transparency and Value-Added Services: Competitive pricing is important, but so is clarity around quotes, lead times, and any additional services (assembly, packaging, logistics, etc.) that can provide added value and streamline your supply chain.
- Customer Service and Communication: Choose a hydroforming supplier that is responsive, transparent, and proactive in addressing your questions, RFQs (requests for quotes), and technical challenges. Effective communication is key to avoiding costly mistakes and ensuring project success.
How Does Hydroforming Compare to Other Metal Forming Techniques?
If you are considering hydroforming for your next project, you may be wondering how it stacks up against traditional metal fabrication processes such as stamping, deep drawing, forging, or machining. Hydroforming stands out for several reasons:
- Reduced Part Count: Hydroforming can combine multiple components into a single, seamless part, minimizing the need for welding or assembly and reducing points of failure.
- Enhanced Design Freedom: Unlike conventional stamping or forging, hydroforming supports the creation of highly complex, organic shapes that are often lighter and stronger.
- Lower Tooling Costs: Fewer and simpler tools are generally required, especially for low- to medium-volume production, making hydroforming ideal for prototyping or product development.
- Superior Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Parts formed via hydroforming can be optimized for load-bearing capacity while minimizing overall mass—a key advantage in industries focused on energy efficiency and performance.
- Excellent Surface Quality: The process results in smooth, high-quality finishes, reducing or eliminating the need for post-processing steps common in other forming methods.
- Faster Time to Market: Streamlined forming cycles, reduced secondary operations, and rapid tooling changes accelerate production and development timelines.
Frequently Asked Questions About Hydroforming
What metals are best suited for hydroforming?
Hydroforming is best suited for ductile, malleable metals such as aluminum, stainless steel, copper, brass, and certain alloys. The process can also be adapted for titanium and specialty metals in advanced aerospace, medical, or defense applications. Material selection depends on the desired mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and final application requirements.
How does hydroforming impact part strength and durability?
Hydroforming produces parts with uniform wall thickness and seamless construction, resulting in high strength, improved durability, and better fatigue resistance compared to welded or mechanically fastened assemblies. The even distribution of forming pressure helps align the metal’s grain structure, contributing to superior mechanical performance.
Is hydroforming cost-effective for small production runs?
Hydroforming is often more cost-effective than traditional stamping or forging for small to medium production runs, due to lower tooling costs, reduced material waste, and the ability to form complex shapes in a single operation. For high-volume production, the cost advantages become even more pronounced as tooling amortization is spread across more parts.
Can hydroforming be used for prototyping?
Yes, hydroforming is particularly well-suited for prototyping and low-volume production. Quick-change tooling, reduced setup times, and design flexibility allow engineers to iterate rapidly and refine product designs before committing to large-scale manufacturing.
What secondary operations are available for hydroformed parts?
After hydroforming, parts can undergo a variety of secondary operations, including trimming, piercing, laser cutting, surface finishing, coating, and precision machining. Many hydroforming companies offer these value-added services to deliver turnkey solutions that streamline your supply chain and reduce lead times.
Choosing the Proper Hydroforming Company
To make sure you have the most constructive outcome when purchasing Hydroforming from a Hydroforming Company, it is important to compare at least 4 or 5 Manufacturers using our list of Hydroforming companies. Each Hydroforming Supplier has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Hydroforming business website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple Hydroforming companies with the same form.
Take the Next Step: Is Hydroforming the Right Solution for Your Project?
Whether you’re looking to produce lightweight automotive chassis components, high-strength aerospace structures, or custom metal parts for industrial or consumer applications, hydroforming offers a proven, flexible, and cost-effective approach. By understanding the various types of hydroforming, their unique benefits, and the critical factors to consider when selecting a supplier, you can confidently move forward with your project and achieve the performance, quality, and value your application demands.
To get started, evaluate your design requirements, target materials, and production volumes. Reach out to qualified hydroforming manufacturers who can provide engineering guidance, prototyping, and full-scale production services. Investing in hydroforming technology can unlock new possibilities in product innovation, manufacturing efficiency, and market competitiveness.








 Cold Headed Parts
Cold Headed Parts Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Metal Spinning
Metal Spinning Powdered Metal Parts
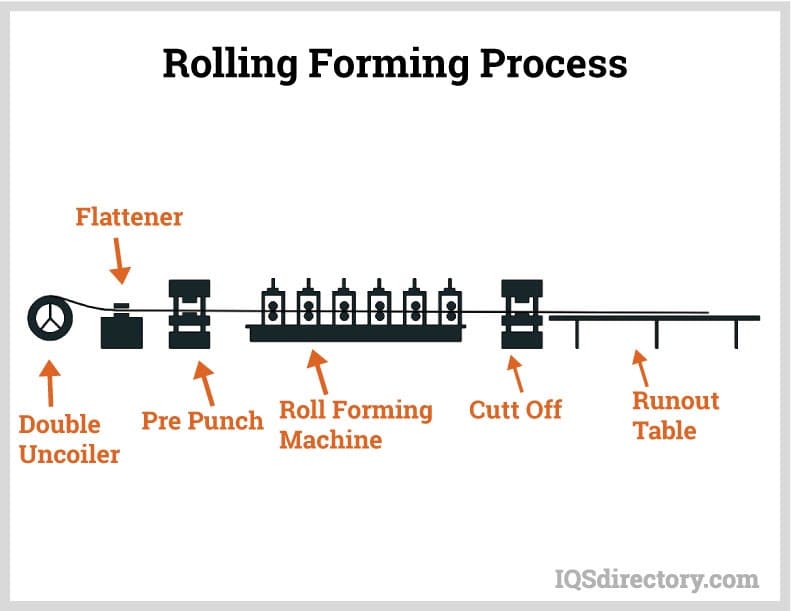
Powdered Metal Parts Roll Forming
Roll Forming Springs
Springs Wire Forms
Wire Forms Wire Mesh
Wire Mesh Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services